🍡 Dango: A Mixed-Initiative Data Wrangling System using Large Language Model
CHI 2025, April 26 - May 1, Yokohama, Japan 🌸
Wei-Hao Chen
Purdue University
Weixi Tong
HUST
Amanda Case
University of Iowa
Tianyi Zhang
Purdue University
Abstract
Data wrangling is a time-consuming and challenging task in a data science pipeline. While many tools have been proposed to automate or facilitate data wrangling, they often misinterpret user intent, especially in complex tasks. We propose Dango, a mixed-initiative multi-agent system for data wrangling. Compared to existing tools, Dango enhances user communication of intent by allowing users to demonstrate on multiple tables and use natural language prompts in a conversation interface, enabling users to clarify their intent by answering LLM-posed multiple-choice clarification questions, and providing multiple forms of feedback such as step-by-step natural language explanations and data provenance to help users evaluate the data wrangling scripts. We conducted a within-subjects user study with 38 participants and demonstrated that Dango's features can significantly improve intent clarification, accuracy, and efficiency in data wrangling. Furthermore, we demonstrated the generalizability of Dango by applying it to a broader set of data wrangling tasks.
To create a data wrangling script, users can first demonstrate their desired actions on the tables in Dango (Step1). They can edit table cells, add/delete/move columns and rows, and copy/cut content across multiple tables. For complex demonstrations, users can also describe their intent in natural language in a chatroom. When ambiguity is detected in a demonstration or a NL description, Dango will generate a multiple-choice question about each unclear part and prompt users for clarification (Step2). Once the ambiguity is resolved, Dango synthesizes a data wrangling script to automate the desired actions. To make it easier for users to understand and validate the synthesized script, Dango explains the script in natural language step by step (Step3). When users notice a wrong step in the script, they can easily fix it by directly editing the NL explanation of that step. They can also add missing steps or delete redundant steps. Dango will update the script based on user edits.
Overview
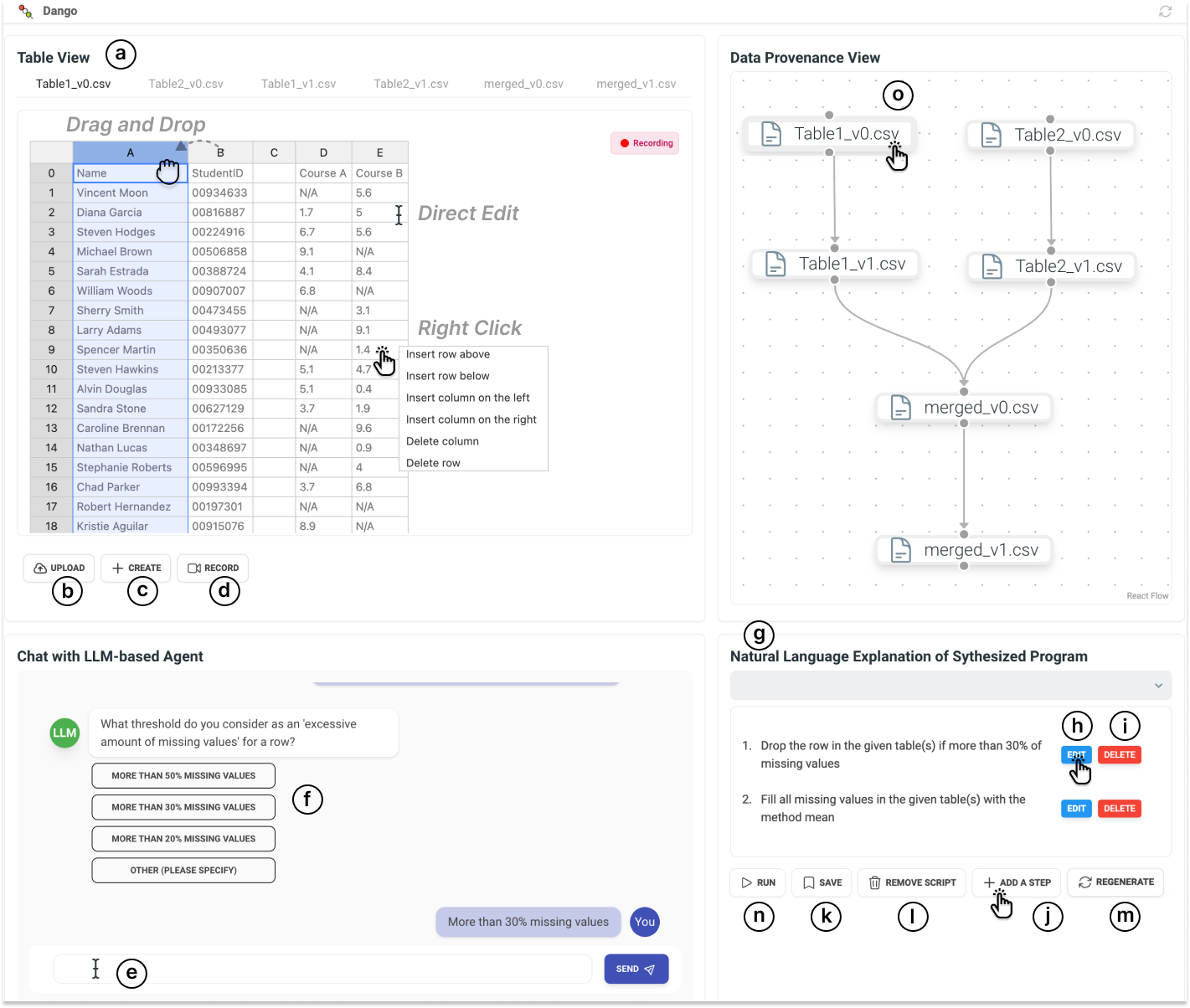
User interface of Dango. In the table view (a), users can upload tables (b) or create new tables (c). Then, they can click the record button (d) and start demonstrating their desired actions. Alternatively, they can express desired actions in natural language in a chatbox (e). Dango will interpret the demonstrations and/or NL descriptions in the backend and generate multiple-choice clarification questions when needed (f). Furthermore, to help users understand and validate the synthesized script, Dango explains it in NL step by step (g). Users can directly edit a step in natural language (h), delete a step (i), add a new step (j), save the script (k), remove the script (l), or regenerate the script (m). Users can click the run button (n) to execute the script on copies of the original tables and verify its behavior without messing up the original demonstrations. Dango also renders a data provenance view to track the transformations performed on each table (o). Users can click table nodes, and the corresponding table content will appear in the table view.
Video Presentation
Citation
@inproceedings{chen2025dango,
title={Dango: A Mixed-Initiative Data Wrangling System using Large Language Model},
author={Chen, Wei-Hao and Tong, Weixi and Case, Amanda and Zhang, Tianyi},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems},
year={2025},
organization={ACM}
}